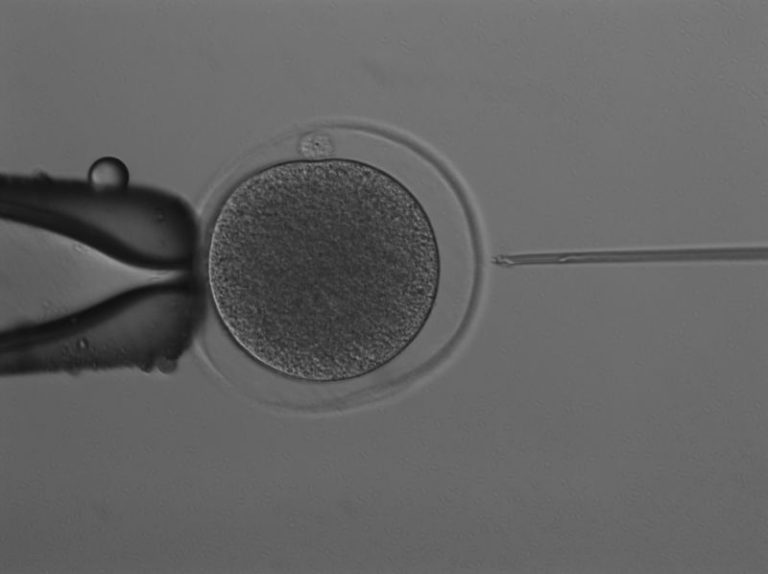
Scientists in Australia have successfully produced the world’s first kangaroo embryo through in vitro fertilization, or IVF, a feat they hailed as a “ground-breaking achievement” that could one day help save endangered species.
The research could be pivotal for Australia’s conservation efforts, given the country’s urgent need to protect its endemic species after having one of the world’s worst extinction records.
Australia has lost at least 33 mammal species since European settlement of the already inhabited continent, according to Australian non-profit Invasive Species Council, a higher rate of extinction than other continent on Earth in recent history.
Scientists at the University of Queensland first assessed how kangaroo eggs and sperm developed in a laboratory, before injecting a single sperm directly into a mature egg, using a technique known as intracytoplasmic sperm injection, the university said Thursday.
Andres Gambini, who led the research into the kangaroo embryo, said the technique could be applied to other animals under the threat of extinction.
“Our ultimate goal is to support the preservation of endangered marsupial species like koalas, Tasmanian devils, northern hairy-nosed wombats and Leadbeater’s possums,” he said, referring to mammals that carry their young in pouches and are an iconic feature of Australia’s unusual fauna.
“Access to marsupial tissues is challenging as they are less studied than domestic animals despite being iconic and integral to Australian biodiversity,” he added.
In 2022, the Australian government announced a 10-year plan to eliminate further extinctions, which included efforts to conserve more than 30% of land mass and protect 110 priority species across the country.
More than 2,200 species and ecosystems in Australia are classified as threatened with extinction, according to a 2023 report by non-profit Australian Conservation Foundation.